Medicine Group 2025 June 14;6(6):646-651. doi: 10.37871/jbres2118.
Gut Microbiota, Cardiovascular Innovation, and Lifestyle Medicine: Southeast Asia’s First Clinical Integration of TMAO Testing
Ali Usman1,2*
2Indonesian College of Lifestyle Medicine, Indonesia
- TMAO
- Regression atherosclerosis
- Restenosis
- Heart failure
- Plant-based diet
- Gut microbiota, Bethsaida Hospital
- Diet adherence monitoring
- Prodia laboratory Indonesia
Abstract
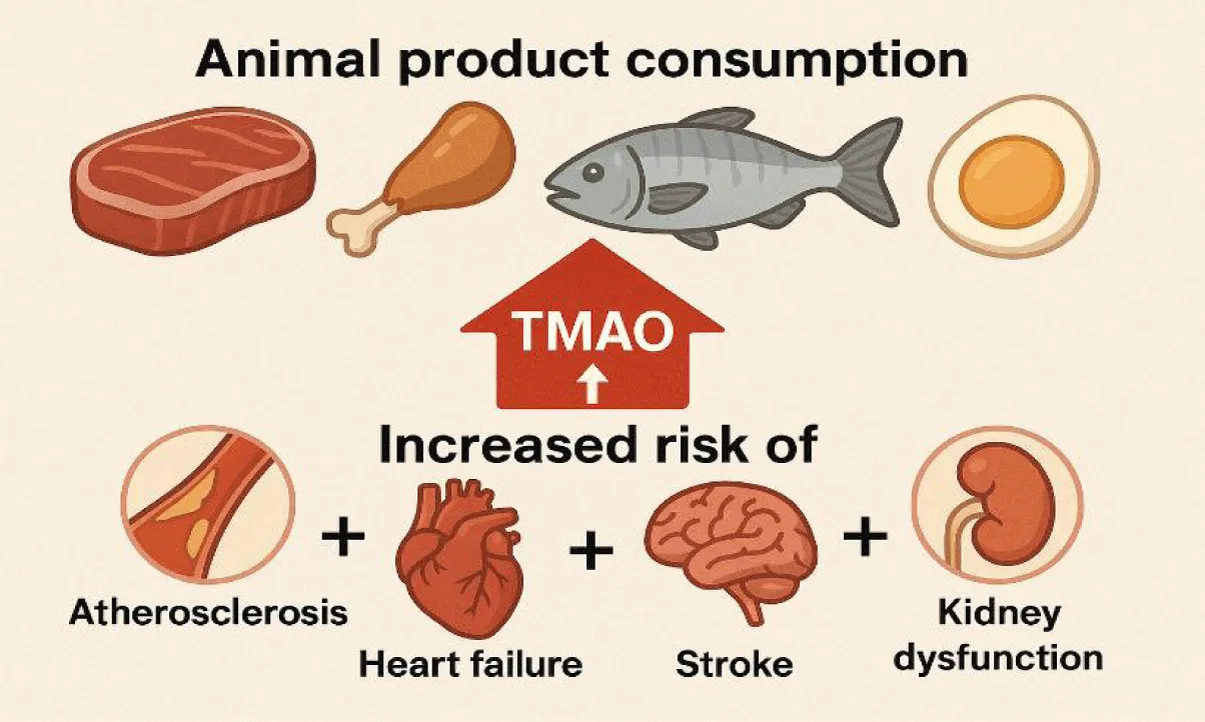
Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) has emerged as a novel biomarker implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of various cardiometabolic conditions, including Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), stroke, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity/metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, restenosis, and heart failure. Despite increasing global recognition of its clinical relevance, TMAO testing was not available in Indonesia until Bethsaida Hospital, under the leadership of Prof. Dasaad Mulijono, successfully established a partnership with Prodia, the only private laboratory in the country willing to invest in TMAO diagnostic technology.
This article describes the implementation of TMAO testing at Bethsaida Hospital, evaluates its diagnostic and prognostic utility, and explores its role in monitoring adherence to a healthy Plant-Based Diet (PBD).
Bethsaida Hospital is also a national pioneer in using Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) technology for coronary interventions. Ongoing research at the institution investigates the relationship between TMAO levels and dietary adherence among cardiac patients. Individuals with lower TMAO concentrations tend to exhibit a reduced restenosis rate following DCB procedures. Furthermore, patients who demonstrate regression of coronary plaques, particularly those adhering to a PBD, consistently exhibit low TMAO levels, supporting its potential as a surrogate marker for a favourable gut microbiota composition and dietary pattern.
TMAO remains the only clinically available biomarker that indirectly reflects gut microbiota health concerning dietary intake, particularly in individuals following a PBD. Its potential application in precision medicine holds promise for enhancing risk stratification, guiding therapeutic interventions, and improving long-term cardiovascular outcomes in patients with cardiometabolic disorders.
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of mortality globally and in Indonesia [1-5]. Traditional biomarkers such as Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) have been helpful but often insufficient to capture the complexity of cardiovascular risk, especially in diet and gut microbiota. TMAO, a metabolite produced by gut microbiota from dietary choline, phosphatidylcholine, and carnitine, has been strongly associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes [6-20]. However, despite its growing significance, access to clinical TMAO testing in Indonesia was non-existent until 2024.
Historical Background
In a determined effort to bring advanced preventive diagnostics to Indonesia, Prof. Dasaad Mulijono initiated collaboration efforts with several major private laboratories. Most declined due to a lack of market awareness and perceived low demand. Only Prodia, Indonesia’s largest private diagnostic laboratory, recognized the potential clinical and scientific value of TMAO and agreed to invest in the equipment and training necessary for high-sensitivity liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) testing.
Bethsaida Hospital subsequently became the first healthcare institution in Indonesia to routinely offer clinical TMAO testing as part of its integrative cardiovascular care strategy.
TMAO and Cardiovascular Disease: Scientific Evidence
Elevated plasma TMAO levels have been independently associated with:
- Atherosclerosis: TMAO promotes foam cell formation and endothelial dysfunction [6,10-15,18,20].
- Restenosis: We postulated that patients with higher TMAO levels after percutaneous interventions are at a greater risk of adverse vascular remodelling and restenosis.
- Heart failure: TMAO exacerbates myocardial fibrosis and ventricular dysfunction [7,17].
These pathophysiological mechanisms are thought to be mediated through pro-inflammatory pathways, disruption of cholesterol metabolism, and altered platelet reactivity [6-20].
Diagnostic Value of TMAO Testing
Sensitivity and specificity [21-23]
- Sensitivity: ~85% for predicting Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) in high-risk patients. Among patients with an increased cardiovascular risk, 85% will exhibit elevated TMAO levels.
- Specificity: ~78%, meaning that 78% of patients without increased CVD risk have normal TMAO levels. Depending on their diet, renal function, and microbiota composition.
False positives [21,24-26]
- High meat, egg yolk, or fish consumption within 24-48 hours of testing.
- Use of certain supplements (e.g., L-carnitine, choline).
- Impaired renal clearance.
False negatives [24,25,27]
- Recent antibiotic use suppresses gut microbiota.
- Acute dietary changes not reflective of long-term patterns, meaning the patient fasted or recently started a PBD (short-term reduction).
- There’s a transient drop due to medications of short-term behaviour changes.
Normal reference range [21,24,26]
- ≤ 6 µmol/L in healthy individuals who usually adhere to a PBD.
- Levels >10 µmol/L suggest increased cardiovascular risk and/or high intake of red meat or animal-based products.
Clinical Application of TMAO at Bethsaida Hospital
At Bethsaida, TMAO measurement is integrated into:
Initial cardiovascular risk screening
Monitoring adherence to a PBD: Sustained TMAO levels within the normal range are used as an objective marker of dietary adherence and gut microbiota health.
Lifestyle intervention programs: Patients transitioning to a PBD typically exhibit a significant reduction in TMAO levels within 4-6 weeks, reinforcing behavioural change.
Research involving patients with atherosclerotic plaque regression: As documented by Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography (CTCA) and invasive coronary angiography.
Research involving patients post-DCB angioplasty: Where TMAO is used to monitor the risk of restenosis.
Our Experiences at Bethsaida Hospital
Initial results at Bethsaida show that patients who adopted a PBD demonstrated a 60-80% reduction in TMAO within 6 weeks, correlating with improved metabolic function and lipid profile. Conversely, patients reverting to animal-based diets experienced re-elevation of TMAO and markers of inflammation [28-37].
Future Directions
- Integration with AI-based dietary recommendation systems.
- Longitudinal studies to track TMAO as a predictor for cardiovascular and chronic disease events in the Indonesian population.
- Broadening role for TMAO as a marker of chronic systemic inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.
Long-Term Applications of TMAO Testing in Broader Clinical Settings
The long-term application of TMAO testing in broader clinical settings holds significant promise for reshaping preventive and therapeutic strategies across multiple specialties. As a non-invasive, metabolically informative biomarker, TMAO testing may evolve into a routine component of annual health check-ups, particularly for populations at risk of cardiometabolic diseases. In cardiology, beyond its current use in assessing restenosis and dietary adherence, TMAO testing could become integral in stratifying patients for aggressive lifestyle or pharmacologic interventions, thus optimizing resource allocation and improving patient outcomes. In nephrology, given TMAO’s accumulation in chronic kidney disease, its monitoring may offer early signals of renal dysfunction or progression risk. In endocrinology, elevated TMAO levels correlate with insulin resistance and systemic inflammation, thus supporting its use as an adjunct marker in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, in oncology, emerging research links gut dysbiosis and elevated TMAO to increased cancer risk, suggesting a future role in screening or prevention strategies. Paediatric and geriatric populations may also benefit from TMAO-guided dietary interventions, which can foster early microbiome optimization and delay age-related decline. As Artificial Intelligence (AI) and precision medicine platforms advance, TMAO values may be algorithmically integrated with genomics, metabolomics, and microbiome profiles to personalize diet plans, forecast disease trajectories, and monitor real-time treatment efficacy. With expanding access and decreasing testing costs, TMAO assessment could become as commonplace as lipid profiling, transforming it from a research biomarker into a standard clinical tool for proactive, nutrition-oriented, and microbiota-driven care across disciplines [38-41].
Conclusion
Bethsaida Hospital has pioneered the clinical use of TMAO testing in Indonesia, thanks to the visionary leadership of Prof. Dasaad Mulijono and a strategic collaboration with Prodia Laboratory. In addition to introducing TMAO testing, we are among the first in the region to adopt DCB technology as part of our advanced interventional cardiology program, with an expanding record of clinical success.
Ongoing research at our centre is focused on the relationship between TMAO levels, adherence to a PBD, and improvements in gut microbiota composition among cardiac patients. Notably, our clinical investigations have demonstrated that patients who maintain low TMAO levels, especially those adhering to a PBD, not only show reduced restenosis rates following DCB angioplasty but also exhibit regression of atherosclerotic plaques, as confirmed by CTCA and invasive coronary imaging.
TMAO offers a unique bridge between gut microbiota, dietary behaviour, and cardiovascular health, enabling a truly integrative and personalized approach to prevention and treatment. Currently, TMAO remains the only widely available clinical biomarker that indirectly assesses the health of the gut microbiota in the context of dietary intake, particularly Polyphenolic Dietary Compounds (PBDs), making it an invaluable tool in lifestyle medicine. Its adoption may set a new paradigm for cardiovascular care in Southeast Asia, supporting long-term prevention strategies rooted in nutrition, microbiota modulation, and individualized care.
Author Contributions
D.M.; Conceptualization, writing, review, and editing.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Di Cesare M, Perel P, Taylor S, Kabudula C, Bixby H, Gaziano TA, McGhie DV, Mwangi J, Pervan B, Narula J, Pineiro D, Pinto FJ. The Heart of the World. Glob Heart. 2024 Jan 25;19(1):11. doi: 10.5334/gh.1288. PMID: 38273998; PMCID: PMC10809869.
- Gaidai O, Cao Y, Loginov S. Global Cardiovascular Diseases Death Rate Prediction. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 May;48(5):101622. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101622. Epub 2023 Jan 29. PMID: 36724816.
- Chong B, Jayabaskaran J, Jauhari SM, Chan SP, Goh R, Kueh MTW, Li H, Chin YH, Kong G, Anand VV, Wang JW, Muthiah M, Jain V, Mehta A, Lim SL, Foo R, Figtree GA, Nicholls SJ, Mamas MA, Januzzi JL, Chew NWS, Richards AM, Chan MY. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases: projections from 2025 to 2050. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024 Sep 13:zwae281. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae281. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39270739.
- Muharram FR, Multazam CECZ, Mustofa A, Socha W, Andrianto, Martini S, Aminde L, Yi-Li C. The 30 Years of Shifting in The Indonesian Cardiovascular Burden-Analysis of The Global Burden of Disease Study. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2024 Mar;14(1):193-212. doi: 10.1007/s44197-024-00187-8. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Erratum in: J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2024 Sep;14(3):1369. doi: 10.1007/s44197-024-00280-y. PMID: 38324147; PMCID: PMC11043320.
- Harmadha WSP, Muharram FR, Gaspar RS, Azimuth Z, Sulistya HA, Firmansyah F, Multazam CECZ, Harits M, Putra RM. Explaining the increase of incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease in Indonesia: A global burden of disease study analysis (2000-2019). PLoS One. 2023 Dec 15;18(12):e0294128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294128. PMID: 38100501; PMCID: PMC10723707.
- Amrein M, Li XS, Walter J, Wang Z, Zimmermann T, Strebel I, Honegger U, Leu K, Schäfer I, Twerenbold R, Puelacher C, Glarner N, Nestelberger T, Koechlin L, Ceresa B, Haaf P, Bakula A, Zellweger M, Hazen SL, Mueller C. Gut microbiota-dependent metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) and cardiovascular risk in patients with suspected functionally relevant coronary artery disease (fCAD). Clin Res Cardiol. 2022 Jun;111(6):692-704. doi: 10.1007/s00392-022-01992-6. Epub 2022 Feb 26. PMID: 35220448; PMCID: PMC9151506.
- Zhou X, Jin M, Liu L, Yu Z, Lu X, Zhang H. Trimethylamine N-oxide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure after myocardial infarction. ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Feb;7(1):188-193. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12552. Epub 2020 Jan 20. PMID: 31960610; PMCID: PMC7083407.
- Guasti L, Galliazzo S, Molaro M, Visconti E, Pennella B, Gaudio GV, Lupi A, Grandi AM, Squizzato A. TMAO as a biomarker of cardiovascular events: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Jan;16(1):201-207. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02470-5. Epub 2020 Aug 10. PMID: 32779113.
- Chen G, He L, Dou X, Liu T. Association of Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Levels with Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality among Elderly Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2022;12(2):39-54. doi: 10.1159/000520910. Epub 2021 Dec 16. PMID: 34915483.
- Canyelles M, Borràs C, Rotllan N, Tondo M, Escolà-Gil JC, Blanco-Vaca F. Gut Microbiota-Derived TMAO: A Causal Factor Promoting Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease? Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1940. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031940. PMID: 36768264; PMCID: PMC9916030.
- Xie G, Yan A, Lin P, Wang Y, Guo L. Trimethylamine N-oxide-a marker for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 24;22(3):787-797. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2203085. PMID: 34565077.
- Lee Y, Nemet I, Wang Z, Lai HTM, de Oliveira Otto MC, Lemaitre RN, Fretts AM, Sotoodehnia N, Budoff M, DiDonato JA, McKnight B, Tang WHW, Psaty BM, Siscovick DS, Hazen SL, Mozaffarian D. Longitudinal Plasma Measures of Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Events in Community-Based Older Adults. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Sep 7;10(17):e020646. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020646. Epub 2021 Aug 16. PMID: 34398665; PMCID: PMC8649305.
- Wang B, Qiu J, Lian J, Yang X, Zhou J. Gut Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide in Atherosclerosis: From Mechanism to Therapy. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 23;8:723886. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.723886. PMID: 34888358; PMCID: PMC8650703.
- Wang M, Li XS, Wang Z, de Oliveira Otto MC, Lemaitre RN, Fretts A, Sotoodehnia N, Budoff M, Nemet I, DiDonato JA, Tang WHW, Psaty BM, Siscovick DS, Hazen SL, Mozaffarian D. Trimethylamine N-oxide is associated with long-term mortality risk: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J. 2023 May 7;44(18):1608-1618. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad089. PMID: 36883587; PMCID: PMC10411925.
- Spasova N, Somleva D, Krastev B, Ilieva R, Borizanova A, Svinarov D, Kinova E, Goudev A. Association of the trimethylamine N-oxide with cardiovascular risk and vascular alterations in middle-aged patients with risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Biosci Rep. 2024 Apr 29;44(5):BSR20232090. doi: 10.1042/BSR20232090. PMID: 38669041; PMCID: PMC12046062.
- Latif F, Mubbashir A, Khan MS, Shaikh Z, Memon A, Alvares J, Azhar A, Jain H, Ahmed R, Kanagala SG. Trimethylamine N-oxide in cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiology and the potential role of statins. Life Sci. 2025 Jan 15;361:123304. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123304. Epub 2024 Dec 11. PMID: 39672256.
- Jarmukhanov Z, Mukhanbetzhanov N, Kozhakhmetov S, Nurgaziyev M, Sailybayeva A, Bekbossynova M, Kushugulova A. The association between the gut microbiota metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide and heart failure. Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1440241. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1440241. PMID: 39391607; PMCID: PMC11464299.
- Yu X, Wang Y, Yang R, Wang Z, Wang X, Wang S, Zhang W, Dong J, Chen W, Ji F, Gao W. Trimethylamine N-oxide predicts cardiovascular events in coronary artery disease patients with diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 18;15:1360861. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1360861. PMID: 39092284; PMCID: PMC11291261.
- Hou CY, Chen YW, Hazeena SH, Tain YL, Hsieh CW, Chen DQ, Liu RY, Shih MK. Cardiovascular risk of dietary trimethylamine oxide precursors and the therapeutic potential of resveratrol and its derivatives. FEBS Open Bio. 2024 Mar;14(3):358-379. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13762. Epub 2024 Jan 21. PMID: 38151750; PMCID: PMC10909991.
- Sun Y, Lin X, Liu Z, Hu L, Sun P, Shen G, Fan F, Zhang Y, Li J. Association between plasma trimethylamine N-oxide and coronary heart disease: new insights on sex and age differences. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 7;11:1397023. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1397023. PMID: 39434851; PMCID: PMC11491342.
- Tang WH, Wang Z, Levison BS, Koeth RA, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Hazen SL. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. 2013 Apr 25;368(17):1575-84. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109400. PMID: 23614584; PMCID: PMC3701945.
- Senthong V, Wang Z, Li XS, Fan Y, Wu Y, Tang WH, Hazen SL. Intestinal Microbiota-Generated Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and 5-Year Mortality Risk in Stable Coronary Artery Disease: The Contributory Role of Intestinal Microbiota in a COURAGE-Like Patient Cohort. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jun 10;5(6):e002816. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002816. PMID: 27287696; PMCID: PMC4937244.
- Cardona A, O'Brien A, Bernier MC, Somogyi A, Wysocki VH, Smart S, He X, Ambrosio G, Hsueh WA, Raman SV. Trimethylamine N-oxide and incident atherosclerotic events in high-risk individuals with diabetes: an ACCORD trial post hoc analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019 Nov 15;7(1):e000718. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000718. PMID: 31798892; PMCID: PMC6861061.
- Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, DiDonato JA, Chen J, Li H, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 2013 May;19(5):576-85. doi: 10.1038/nm.3145. Epub 2013 Apr 7. PMID: 23563705; PMCID: PMC3650111.
- Cho CE, Caudill MA. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide: Friend, Foe, or Simply Caught in the Cross-Fire? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Feb;28(2):121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Nov 5. PMID: 27825547.
- Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, Koeth R, Levison BS, Dugar B, Feldstein AE, Britt EB, Fu X, Chung YM, Wu Y, Schauer P, Smith JD, Allayee H, Tang WH, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2011 Apr 7;472(7341):57-63. doi: 10.1038/nature09922. PMID: 21475195; PMCID: PMC3086762.
- Velasquez MT, Ramezani A, Manal A, Raj DS. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Toxins (Basel). 2016 Nov 8;8(11):326. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110326. PMID: 27834801; PMCID: PMC5127123.
- Mulijono D, Hutapea AM, Lister INE, Sudaryo MK, Umniyati H. Mechanisms of plant-based diets reverse atherosclerosis. Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine. 2024;8(4):290-302. doi: 10.26502/fccm.92920390.
- Mulijono D. Plant-Based diet in regressing/stabilizing vulnerable plaques to achieve complete revascularization. Archives of Clinical and Biomedical Research. 2024;8(3):236-244. doi: 10.26502/acbr.50170405.
- Mulijono D, Hutapea AM, Lister INE, Sudaryo MK, Umniyati H. How a Plant-Based Diet (PBD) Reduces In-Stent Restenosis (ISR) and Stent Thrombosis (ST). Cardio Open. 2024;9(1):01-15. doi: 10.33140/COA.09.01.05.
- Mulijono D, Hutapea AM, Lister INE, Sudaryo MK, and Umniyati H. Plant-Based diet to reverse/ regress vulnerable plaque: A case report and review. Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports. 2024;8(3):126-135. doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550674.
- Mulijono D. Bethsaida hospital: Pioneering plant-based diet and lifestyle medicine revolution in Indonesia. Arch Epidemiol Pub Health Res. 2025;4(1):01-03. doi: 10.33140/AEPHR.04.01.02.
- Mulijono D. Prof. Dasaad Mulijono: The plant-based guru redefining cardiology and preventive medicine. On J Cardio Res & Rep. 2025;8(1). doi: 10.33552/OJCRR.2025.08.000676.
- Mulijono D. Healing with food or managing with injection? A new era in chronic disease care. J Biomed Res Environ Sci. 2025;6(4):373-377. doi: 10.37871/jbres2092.
- Mulijono D. How a plant-based diet and ultra-low ldl levels can reverse atherosclerosis and prevent restenosis: A breakthrough in heart health. J Biomed Res Environ Sci. 2025;6(4):368-372. doi: 10.37871/jbres2091.
- Mulijono D. Reclaiming healing through nutrition: Resistance to plant-based diets and the biblical call to restoration. Arch Epidemiol Pub Health Res. 2025;4(2):01-03. doi: 10.33140/AEPHR.04.02.01.
- Mulijono D. What was meant for harm. A testimony of healing, faith, and medical revolution. Arch Epidemiol Pub Health Res. 2025;4(2):01-05. doi: 10.33140/AEPHR.
- Gatarek P, Kaluzna-Czaplinska J. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) in human health. EXCLI J. 2021 Feb 11;20:301-319. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-3239. PMID: 33746664; PMCID: PMC7975634.
- Jaworska K, Kopacz W, Koper M, Ufnal M. Microbiome-Derived Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) as a Multifaceted Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease: Challenges and Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 21;25(23):12511. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312511. PMID: 39684223; PMCID: PMC11641139.
- Liu J, Ge P, Luo Y, Sun Z, Luo X, Li H, Pei B, Xun L, Zhang X, Jiang Y, Wen H, Liu J, Yang Q, Ma S, Chen H. Decoding TMAO in the Gut-Organ Axis: From Biomarkers and Cell Death Mechanisms to Therapeutic Horizons. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Apr 29;19:3363-3393. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S512207. PMID: 40322030; PMCID: PMC12049683.
- Caradonna E, Abate F, Schiano E, Paparella F, Ferrara F, Vanoli E, Difruscolo R, Goffredo VM, Amato B, Setacci C, Setacci F, Novellino E. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) as a Rising-Star Metabolite: Implications for Human Health. Metabolites. 2025 Mar 24;15(4):220. doi: 10.3390/metabo15040220. PMID: 40278349; PMCID: PMC12029716.
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.