Environmental Sciences . 2022 December 09;3(12):1471-1477. doi: 10.37871/jbres1621.
Regulations and Plans to Reduce Climate Change in Ukraine
Delehan Svitlana Vasulivna1* and Melehanych Hanna Ihorivna2
2Associate Professor, Department of Political Science and Public Administration, State Higher Educational Establishment Uzhhorod National University, Ukraine
The development of global industrial production, increasing the intensity of labor in order to increase the volume of production of goods and services, the production of food products and meeting the needs of society have become prerequisites for global warming and an increase in carbon emissions into the atmosphere.
Carbon generation is not limited to just one sector of the economy and is the result of the work of energy, agriculture, industrial production, construction, logistics and transport, the work of Information Technology (IT) sector and other industries.
The governments of countries around the world are constantly looking for new ways to manage and reduce the negative consequences of carbon emissions by analyzing current state policies, forming climate-responsible business behavior, developing production reorientation strategies, adopting appropriate legislation, applying stimulating and restrictive instruments of influence for conducting economic activities, taking international obligations and global reorientation of the economy.
The mechanisms of reorientation of the economy are different from a decrease in the level of industrialization of production to the transformation of a negative factor into a market that reached the equivalent of more than 200 billion dollars.
However, emissions of Carbon dioxide (CO2) in the world are increasing every year. According to the joint research center of the European Commission, their figures rose to 38 billion tons.
Until the middle of the 20th century, the leaders of CO2 emissions were the United State of America (USA) and Europe, but the second half of the century was marked by a significant increase in emissions in Asia. Today, the USA and Europe account for slightly less than one-third of emissions.
The world is working to reduce its CO2 emissions, but the problem will remain acute and relevant for a long time and will require maximum attention from society.
Ukraine is a strategic partner of the European Union (EU) and the European direction of state policy in achieving the goal of carbon neutrality and introducing modern mechanisms for reducing and absorbing CO2 emissions in all areas. That is one of the priorities for Ukraine in the context of the European integration process. The war in Ukraine is one of the reasons for the nowadays world economic crises and for sure next years for Ukraine will be years of changes: new legislation, a new economic system, and new rules of industry, business, and style of life.
As a part of the United Nations (UN) framework convention on climate change and Kyoto protocol, Ukraine ensured its obligations under international agreements, but for a long time it was not in this matter for a holistic policy, actions and decisions were fragmented mainly within environmental policy or even within the framework of civil society activity. Significant shifts have taken place in the last five years. Thus, in 2017, Ukraine's energy strategy was approved for the period up to 2035 “safety, energy efficiency, competitiveness”, which became a software document in the development of the fuel and energy complex of Ukraine. It is important to note that the energy strategy envisages the completion of the energy sector reform and integration with the EU energy complex by 2025 [1]. However, work on the new document is currently underway by 2050. In 2018, the cabinet of ministers of Ukraine adopted a strategic document on the transition of the Ukrainian economy to a model of low carbon development, which provides for a decrease in the volume of greenhouse gas emissions, rejection of fossil fuels and the start of investing in renewable energy sources. This strategy of low carbon development of Ukraine by 2050 determines the national vision conceived by the interested parties to separate the further economic growth and social development of the state from increasing greenhouse gas emissions. For Ukraine, this is the first experience of using a synergistic approach, since solving climate change requires significant changes in key sectors of the economy and the main components of human life. This strategy, on the one hand, relies on national priorities of sustainable development and the current strategy for the development of economic sectors, and on the other hand, determines the possible trajectory of economic growth, considering the goals of state policy to reduce emissions and increase greenhouse gas absorption. At the national level, this document is a tool of public administration and the formation of climatic responsible behavior of businesses and citizens, and at the international level supports the global purpose of stabilizing the concentrations of greenhouse gasses in accordance with the scenario of maintaining the growth of global average temperature within less than 2°C from the pre-industrial level. The presence of a strategy for low carbon development of Ukraine is the basis for the development and implementation of economic tools for supporting Ukraine's transition to low-carbon development, attracting innovative, highly efficient technologies and investments [2].
In 2019, the law of Ukraine “on the basic principles (strategy) of the State. Environmental policy of Ukraine for the period up to 2030" was adopted. This document is focused on ensuring energy efficiency, increasing the production of green energy, the introducing of low-carbon production technologies, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reducing pollution of reservoirs. However, the issue of climate change is not sufficiently highlighted in this document. Therefore, in response to the environmental requirements of the world community, Ukraine's international obligations under the Paris climate agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the consequences of global change in the climate of Ukraine, the cabinet of ministers of Ukraine adopted a strategy of environmental safety and adaptation to climate change by 2030. On October 20, 2021 it is designed to increase the level of environmental safety, reduce of impact and effects of climate change in Ukraine. The main environmental threats to Ukraine are identified in the document: a significant level of air pollution, water and land resources, imperfect state supervision (control) system and environmental monitoring. There is also a critical situation with the formation, accumulation, storage, processing, and disposal of waste. According to the strategy, the most vulnerable to the consequences of climate change in Ukraine are social economic sectors such as biodiversity, water resources, energy, public health, forestry, coastal territories, fisheries, agriculture, soils, etc. And they will be aimed at the main activity of the government in the framework of the document. In addition, Ukraine's activities in this area are formed on the European integration vector of development. In particular, a number of articles are devoted to this in the Association. Agreement between Ukraine, on the one hand, and the European Union, the European atomic energy community and their member states, on the other. In addition, Ukraine has committed itself to the 22nd EU-Ukraine Summit in October 2020 as part of a European green course. It is known that this document aims to move Europe to a climatic-neutral continent by 2050 [3]. However, regarding the policy of the state at the national level, despite all the above documents, it is not clear. There are UN recommendations that have not yet been implemented in Ukraine in the field of environmental protection programs, and some provisions of the Kyoto Protocol remain unfulfilled [4].
On July 26, 2022, the European Commission published its next annual report on Ukraine's implementation of the Association Agreement with the EU for 2021 [5]. The main conclusion in the context of the European green course is disappointing: despite progress in climatic reforms, in the environment, progress was insignificant. Many obligations are still in the early stages of implementation, including the emission trade system and the implementation of the National Emission Reduction Plan from large burning factories. The European Union also considers it a gross violation of the Association Agreement for the restriction of exports of timber.
Among the achievements that were in the report:
- Approval and submission of an updated national contribution under the Paris agreement.
- Adoption of environmental safety and adaptation to climate change.
- Dialogue on the European green course.
- Preparation of by-laws in the field of organic production.
- Adoption of the state forest management strategy.
- Adoption of the law on restriction of plastic circulation.
- The beginning of the work of the mechanism of the Monitoring, Reporting and Verification (MRV) of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Introduction of promising CO2 tax rates.
The negative evaluation was given to:
- Slight progress in the implementation of a new fishing policy.
- Proposals of the ministry of energy to postpone the implementation of measures of the national plan for reducing emissions from large factories, as well as the lack of its financing plan.
- Deviation of the project of the law on industrial pollution.
- Slow progress in accepting the national energy and climate plan.
- Lack of real steps on climate change.
- The backwardness of the emission trade system [6].
The report also deals with the adoption of a framework law on waste. Simultaneously the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine adopted in the second reading the project of law no. 2207-1-d "on waste management" [7]. It is a framework bill in the field of waste management, which creates a waste management system by analogy with a system that exists in the European Union member states. In particular, the bill lays the framework for the implementation of the principle of expanded liability of waste manufacturers, which will be a key to solving several environmental problems and improving the situation with the accumulation of household waste. Yes, the bill lays foundations for separate waste collection, processing, and subsequent use. Thus, the waste will be a resource that will open opportunities to attract investments to create separate waste collection and waste management systems, not just a dangerous factor for the environmental situation in the country.
Achievements in Ukraine in general environmental protection and climate change can be evaluated by various reports. For example, the German Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) German watch, New Climate Institute and Climate. Action Network annually measures the achievements of countries in the form of the "climate change productivity" Index in 4 categories (14 indicators): greenhouse gas emissions (40%), renewable energy (20%), energy use (20%) and climate policy (20%). According to this indicator of 2022, Ukraine ranks 20th out of 64, where the first three are not defined. The ratio of indicators is the emissions of greenhouse gasses (27.3%), renewable energy (7.13%), energy use (18.32%) and climatic policy (7.70%) [8].
Each country uses general and specific indicators to evaluate environmental trends. For global comparison, the most complete methodology is a methodology developed by the University of Yale in the United States, which provides the calculation of a complex index, namely the environmental efficiency index. This is a global study of how states fight the environment and help develop ecosystems (from nature to environmental policy). The final estimate of the country and its place in the rating is the average total value of 32 parameters. For each country, it was graded from 1 to 100. Ukraine took 52nd in 2022. In general, the situation in the world is improving - such a contradictory conclusion is made by the rating. In 2022, most people have access to drinking water and use sewage systems, and the nitrogen dioxide content decreases in the atmosphere. But there remains the poor quality of wastewater treatment and the atmosphere from carbon dioxide release [9].
The illegal annexation of Crimea in 2014 led to significant environmental consequences that challenged the ecological safety of the Crimean Peninsula, and the state of the environment of the Black and Azov seas. This was published in February 2022 as part of a study by experts of the Center for Defense Strategies (CDS) with the financial support of the United Kingdom (UK) government in the framework of the Project “consolidation of the Crimean platform for improving the framework of Ukrainian and international policy on the de-occupation of Crimea (phase II)” [10]. In addition, the full-scale invasion, and the war of Russia in the territory of Ukraine do not make optimistic forecasts, since explosions, fires and the use of different types of weapons clearly adversely affect most of the indicators and some of which will not even be able to be measured. In addition, martial law in the country also affects the country's economy directly.
The experience in combating climate change shows the most successful and effective activities of European countries, within the framework of environmental diplomacy. Today, environmental diplomacy is a significant tool for implementing the international environmental protection mechanism. At the present stage of globalization and in the accounting of all the seriousness of environmental problems, which require the attraction of more and more actors, multilateral agreements are the most common practice in environmental diplomacy. The main administrative tools of European environmental policy are such normative acts and documents as conventions and directives, as well as regulations. Conventions, especially adopted under the auspices of the UN, are an important tool for global environmental policy. Thus, Directive 85/337/EU on June 27, 1985, assessing the influence of some state and private environmental projects on both international legal cooperation in the field of environment and environmental legislation of different countries that are not members of the European Union at all. The basic idea of the principle of preventive actions of the directive is that environmental protection actions should be carried out in advance and aimed at eliminating the immediate adverse source and preventing its appearance. In accordance with Art. 1 directive any state or private economic project capable of affecting the environment must undergo an appropriate expert environmental assessment. Since the 1990s, the EU's ecological policy has affected the departure from direct administration to more flexible, which includes market elements, mechanisms (for example, the trading of greenhouse gas emissions and the elements of party management, based on the principle of "divided responsibility" between participants-government, business, public, consumers) [11].
Based on the report of the European Agency on the environment, one can cite the following classification of modern existing market instruments:
- Trade permits entered to reduce emissions (eg; CO2 emissions) or natural resources savings (eg; fish catches).
- Environmental taxes are introduced to change prices and thus consumers and producers.
- Environmental contributions, entered to fully or partially cover the costs of environmental services, measures to reduce pollution of water resources, for the burial of waste.
- Environmental subsidies and benefits are created to stimulate the development of new technologies, create new markets for ecological goods and services, as well as to maintain high levels of environmental protection companies.
- Responsibility and compensation schemes, the purpose of which is to provide adequate compensation for the effects of environmental activities, as well as the cost of preventing and restoring the damage.
The risks and effects of climate change can be reduced within certain limits if people and nature adapt to changing conditions. The extent of climatic risks (adaptation) has increased worldwide. Individuals and households, together with communities, enterprises, religious groups, and public movements, are already adapting to climate change. The report also emphasizes that the effectiveness of available adaptation options is reduced with every step of warming. Successful adaptation requires urgent, more ambitious, and accelerated actions and, at the same time, a rapid and deep reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
It is most natural to replace fossil coal with firewood, woody briquettes, or pellets. But the replacement of coal with firewood and various wood waste does not solve the problem of reducing emissions into the atmosphere. Now, there is also no positive experience of replacing fossil fuels with different types of biomasses. Biomass burning in the world causes 32% carbon monoxide emissions, and 50% high-carcinogenic polyaromatic hydrocarbons [12].
Because climate issues are inextricably linked to the environment, especially to the atmospheric air, measures to counteract climate change are mainly focused on environmental protection against harmful effects and this activity can be leisure, preventive, control, stimulating, renewable and prohibited (Figure 1) [13].
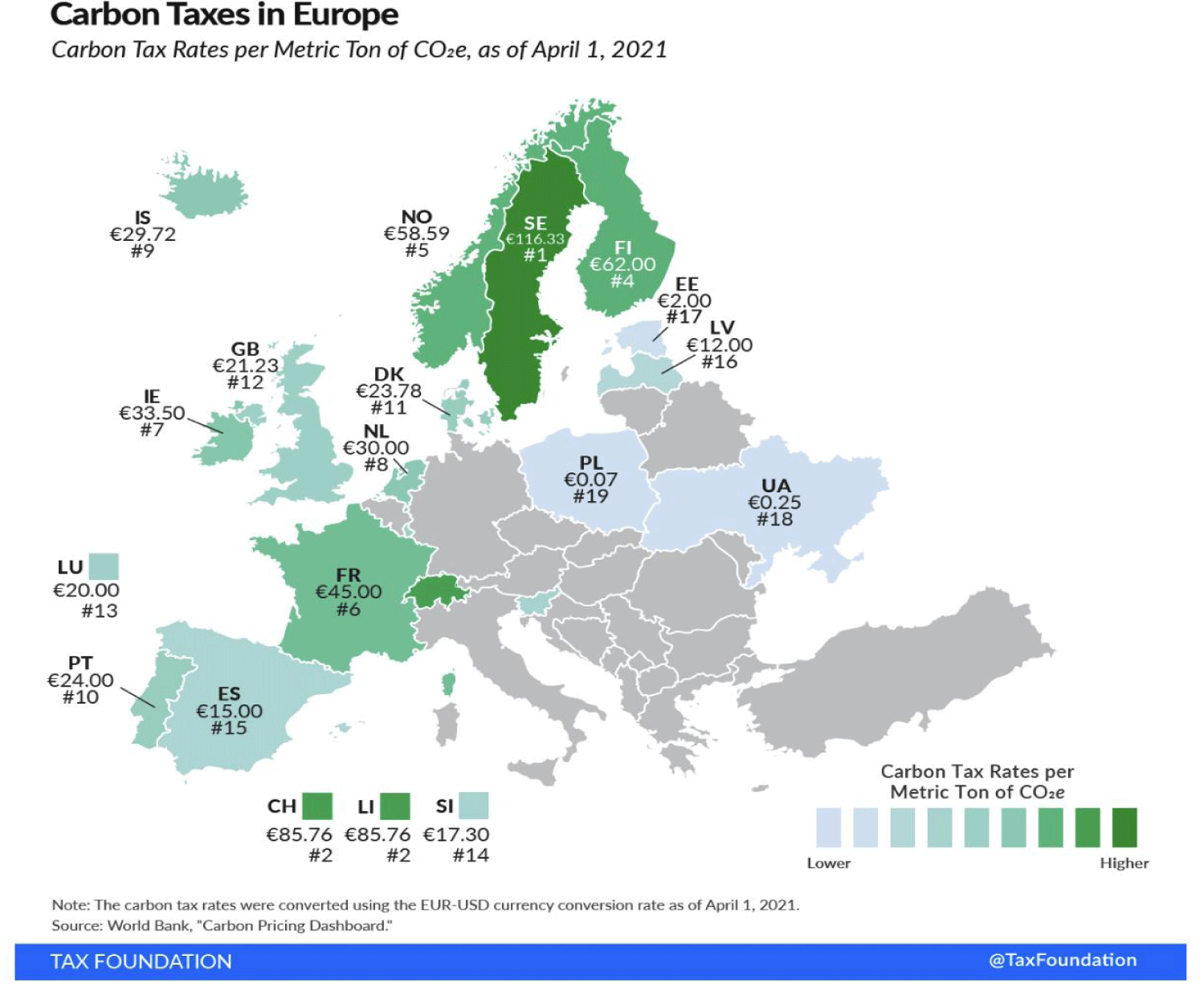
One of the common measures to influence manufacturers is carbon or carbon tax. It is pulled from the carbon content in fuel, usually in the transport and energy sectors. Carbon taxes are a form of carbon pricing. This term is also used to indicate the equivalent tax on carbon dioxide emissions, the latter of which is very similar, but can be applied to any type of greenhouse gasses or combinations of greenhouse gasses released by any sector of the economy to prevent climate changes in the European Commission (EC). They developed a package of fit for 55 proposals, which was published on July 14, 2021. These new proposals are the introduction of a mechanism of border carbon adjustment (carbon border adjustment mechanism). Experts call this tax one of the key reform points. It provides for the collection of fees from imported EU goods, depending on their carbon trail [14].
For Ukraine, the development and transformation of the national economy should be a departure from an outdated model, implementation of measures to reduce the energy intensity of the economy, as well as diversification of sources and ways of supply of energy resources, energy and environmental safety, improvement of economy and optimization of energy balance [15].
The refusal from the energy-intensive industry and the use of fossil fuels is critical for the effort to reduce climatic changes - both in Ukraine and around the world.
Decarbonization is an urgent need to restrain the temperature. In 2021, the Government of Ukraine approved a new climatic target: by 2030, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 65% compared to 1990. This has become our updated nationally defined contribution to the Paris Agreement.
In 2020, the national coal regions transformation program was announced, which includes protection of the coal industry reform. Its purpose is to reduce the volume of coal use in energy, diversification of the economy of coal regions, the creation of new points of economic growth and replacement of revenues from coal enterprises [16]. In 2021, the reforms of ministry of energy of Ukraine were established as a permanent advisory and advisory body of the ministry of energy of Ukraine, which was created to support the ministry in the development and implementation of reforms in the energy sector of Ukraine.
The main directions of office work are:
- Integration of energy markets with the EU.
- Decarburization and renewable energy sources.
- Energy security.
- Corporative management.
- Reasonable use of energy.
The reform support team provides analytical support to the Ministry in the formation of politicians, participates in the development of proposals for reforms of the energy sector of Ukraine, as well as projects of relevant legislative acts, and promotes the institutional capacity of the Ministry of Energy.
As mentioned earlier, work on the new energy strategy of Ukraine until 2050, as well as the green course of Europe, is ongoing. The ministry of energy of Ukraine has involved international technical assistance in the development of energy strategy and the UK government has joined the process.
The Paris agreement aimed at increasing the global response to the threat of climate change in the context of sustainable development and eradication of poverty.
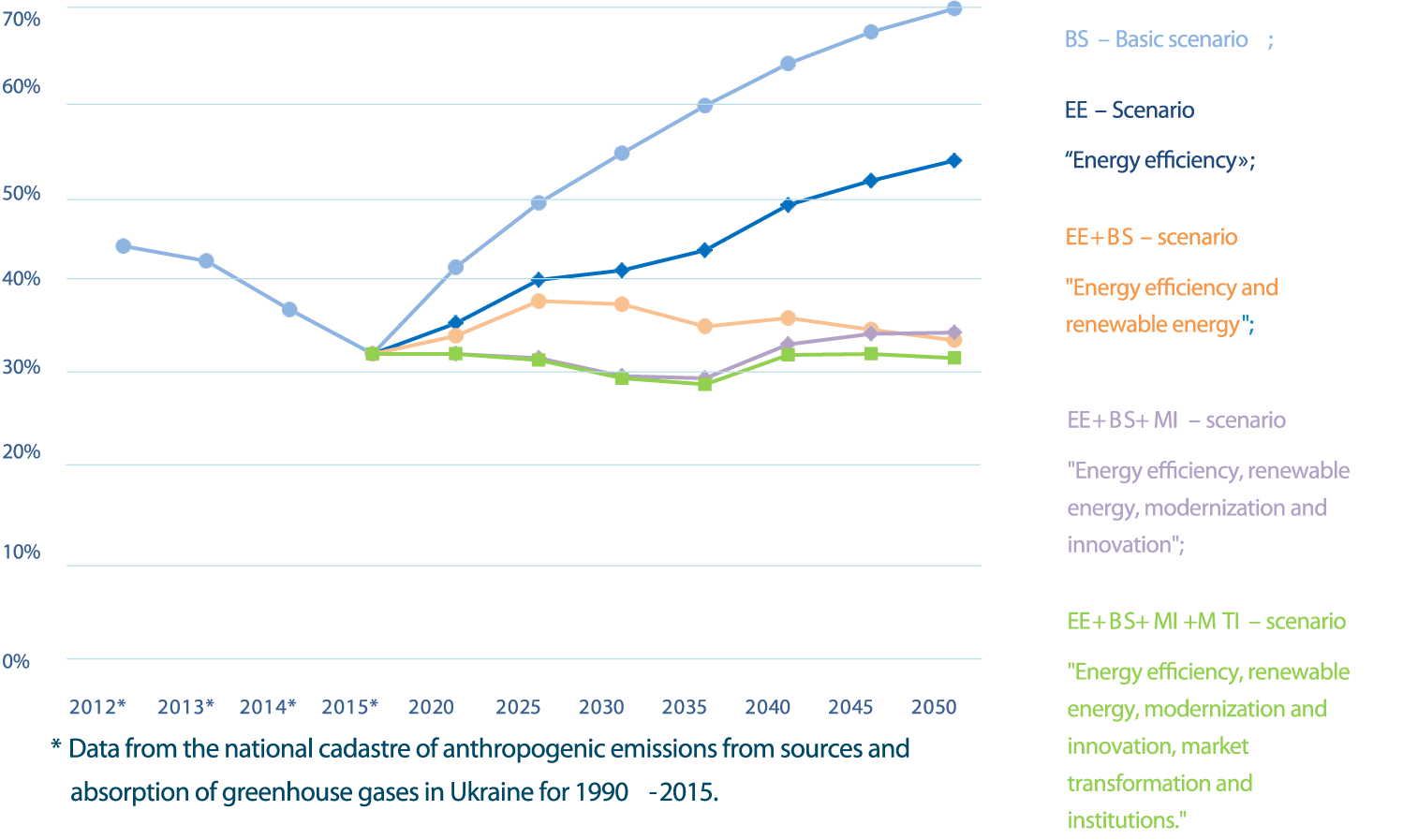
In Ukraine, achieving the optimal goals of the Paris agreement with national priorities will allow:
- Increase the role of energy efficiency and general technological modernization of the economy in compliance with the principles of sustainable development (BS-Basic scenario).
- Widely substantiated the introduction of renewable energy sources (ЕЕ-scenario Energy efficiency).
- Will ensure the public policy in the field of climate change and strategies, politicians, plans and programs in other areas of economic and social development of the state (ЕЕ+ВS-scenario “Energy efficiency and renewable energy").
- Introduction of the latest economic instruments to achieve the nationally significant contribution of Ukraine to the Paris Agreement in an optimal way (ЕЕ+ВS+МІ+MТІ-scenario "Energy efficiency, renewable energy, Modernization and Innovation(МІ), Market Transformation and Institutions (MТІ).
- Creation of grounds for attracting climate investments in the economy of Ukraine (ЕЕ+ВS+МІ+MТІ).
- Increasing the role of Ukraine in the international fight against climate change (ЕЕ+ВS+МІ+MТІ).
The forecast dynamics of greenhouse gas emissions in the energy and processes sectors compared to 1990 (1990 = 100%) in the base and alternative scenarios are given (Figure 2).
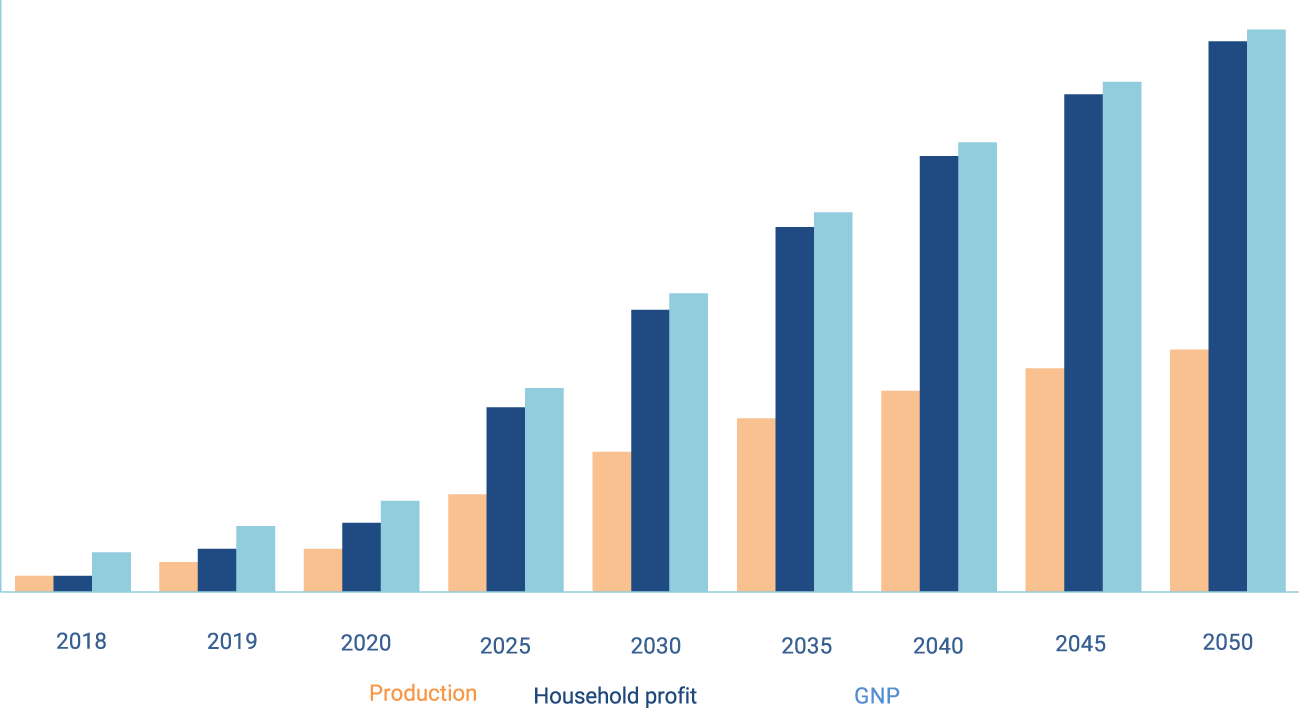
Assessments of the economic consequences of the implementation of politicians and measures of low-carbon development indicate that their implementation is generally characterized by positive macroeconomic consequences (Figure 3). The main factor in qualitative changes is the intensification of investment processes, which, in turn, leads to an increase in production efficiency due to a decrease in the specific consumption of energy resources. Due to the increase in productivity of technologies and production processes, there is an additional increase in the production of goods and services (6%) and Gross National Product (GNP 13%) by 2050.
Decarbonization was one of Ukraine's energy priorities, but Russian aggression has made this approach even more urgent. We strive to have one of the "greening" energy production sectors in Europe after implementing a decarbonization strategy.
Over the last 6 months, because of the war between Russia against Ukraine, Ukrainian metallurgy has lost 30% of its assets. About a hundred enterprises were damaged or destroyed, among them - the metallurgical factory "Azovstal", Mariupol Illich metallurgical factory and Avdiivka coke chemical factory.
Now the mission of Ukraine's energy strategy by 2050 is to create conditions for the sustainable development of the national economy by ensuring access to reliable, sustainable, and modern energy sources. Because of the war in Ukraine today one of the first priorities of the state is energy independence [17]. As a result Ukraine's energy strategy also provides for a significant expansion of biomass and biofuel production. According to analysts, Ukraine can generate 6-8 billion cubic meters of biomethane by 2050. Biomethane retains the benefits of natural gas and can be used for thermal and electrical generation, industry and transport. In this case, it is carbon neutral. By 2050, the energy sector should be as close as possible to climatic neutrality. This will mean the presence of pure energy, overcoming energy poverty, the development of an innovative and decentralized power system, the full functioning of national energy markets and their integration into international ones.
The key principles of Ukraine's energy strategy are economic validity, environmental friendliness, accessibility, social justice, and the market. The energy strategy will be based on the target indicators of economic development in accordance with the national economic strategy for the period up to 2030. And also, on the international obligations made by Ukraine - first of all, under the agreement on the association of Ukraine with the EU and under the Paris climate agreement.
The goals of Ukraine's energy strategy 2050 are:
- Achieving the maximum level of climatic neutrality.
- Maximum reduction of coal use in the energy sector.
- Update and modernization of energy infrastructure.
- Increasing the efficiency of using resources in the energy sector.
- Comprehensive integration with the European Union markets and the effective functioning of domestic markets.
- Provision of the energy sector with its own resources taking into account economic feasibility.
- Development of alternative energy sources, new products and innovative solutions in the energy sector [18].
The energy sector of Ukraine refers to the list of countries that have set sufficient goals to reduce emissions. The purpose of Ukraine is to reduce emissions to a level at which they will not exceed 60% of 1990 indicators. In fact, the reduction of emissions in Ukraine compared to 1990 is not so much due to the modernization of the economy and the implementation of energy-efficient programs, but in connection with de-industrialization. It should be noted that in the plan of law work for 2022 there are 62 bills concerning the topic of a pure environment, which is 1/10 of the whole list of issues that require legislative regulation [19]. Today, Ukraine faces new challenges and environmental problems because of military operations. Therefore, existing strategies for decarbonization will no longer be relevant.
References
- Order on the approval of Ukraine's energy strategy for the period up to 2035 “safety, energy efficiency, competitiveness”.
- Strategy low carbon development of Ukraine 2050.
- Association agreement between Ukraine, on the one hand, and the European Union, European atomic energy community and their member states, on the other hand.
- Glukh M, Abbasova K. Climate change as a problem of planetary nature: the Paris climate agreement-a global humanities initiative.
- Joint staff working document. Association implementation report on Ukraine.
- Ukraine: EU report notes important steps taken in the implementation of the reform agenda.
- The law of Ukraine about waste management.
- Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI).
- Experts named the greenest countries in the world. 2022.
- Vasyliuk O. Degradation of the environment of the black sea and Azov seas as a result of the annexation of crimea. 2022.
- Gabro I, Shevchuk O. Tools of EU environmental diplomacy.
- Krutoholova I, Braverman V. Economical and ecological aspects of decardonization of the energy industry. Economy and Society. 2022;(38).
- Kopytsia I, Ohienko M. Concepts for the development of societies scientific potential. 2021. doi: 10.51582/interconf.21-22.11.2021.036.
- Bilozerova L. The EU carbon tax will be an impetus for the decardonization of the Ukrainian economy. 2021.
- Levchenko N, Antonova L. State regulation of energy transformation processes from an outdated model of its functioning to the latest “Low-Carbon” model. Public Administration and Regional Development. 2020. doi: 10.34132/pard2020.10.12.
- Transformation of the coal regions. Ministry of energy of Ukraine.
- Demchenkov Ya. Strengthening Europe. How the EU will give up Russian hydrocarbons and how Ukraine will help.
- Energy strategy.
- Decree of Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine about the plan of legislative work of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine for 2022.
Content Alerts
SignUp to our
Content alerts.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.